In this tutorial we will see what is Data binding , how it works and how many types of data binding is there in angular.
Data binding is a core concept of angular which is used to synchronized the data between model and view. So whenever there is any updation in the view , component gets updated.Similarly if there is any updation in component then view gets updated. It is one of the most powerful and important features in any software development language. Using Data Binding, the user will be able to manipulate the elements present on the website using the browser. Therefore, whenever some variable has been changed, that particular change must be reflected in the Document Object Model or the DOM.
Types of Data Binding –
- String Interpolation
- Property Binding
- Event Binding
- Two-Way Data Binding
Have a look into below diagram.
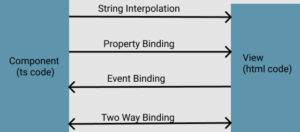
From above diagram you can see that –
- String Interpolation , Property Binding and Event Binding is a one way data binding , which means data flow from one direction. So in string interpolation and property binding data is flowing from component to view where as in event binding data flows from view to component.
- Two way data binding means data flow in both the direction means from view to component and from component to view.
Lets have a detailed look into each binding-
1. String Interpolation : Its a one way data binding. Data flows from component to view. It is represented by double curly braces {{}}. Between these curly braces we have to bind the data. For example –
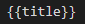
here title is a variable which is defined in ts file.
2. Property Binding : It is also a one way data binding. Thus it allows you to change the value whenever you want but only at the component level. whenever there is any value change at the component level , the view gets updated. It is represented by square bracket [].
![]()
Here disabled property is inside the square bracket hence it is representing as a property binding. currentValue is variable defined in ts file. When we communicate between parent to child component then also we use the property binding.
3. Event Binding : Its also a one way data binding. But its just opposite of string interpolation and property binding because in event binding data flows from view to component. Event binding is defined as the updating/sending of the value/information of a certain variable from the presentation layer (view) to the component (model). Event Binding is represented by (). For example – click on button, change the dropdown value. Have a look into below code.
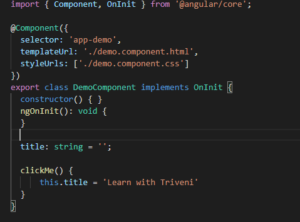
In this file we have defined title variable with blank value, and when clickMe() method will call that time we are assigning the new value to title.
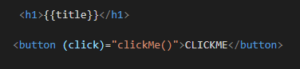
And here on button click we are calling clickMe() method and binded the value of title in h1 tag. So once button will click value of title will be “Learn with Triveni”.
When there is a communication between child component to parent component then also we use the event binding to handle the emitted data from child component.
4. Two-Way Data Binding : Two-way data binding is a combination of both Property and Event binding and it is a continuous synchronization of a data from view to the component and component to the view, i.e. changes made in the component’s data should sync to the view and should immediately update the model into the corresponding component with view data. By using ngModel directive we can implement the two way data binding. ngModel is a combination of property binding and event binding i.e [(ngModel)]. To use the ngModel it is must to import the FormModule in app.module.ts file. Lets have look into below example –
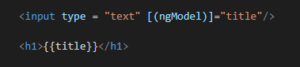
here you can see we have bind the title inside the ngModel directive and title is variable defined in the ts file.
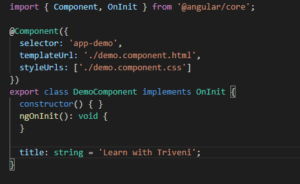
so initially textbox value will be “Learn with Triveni”. And if you will change the value of textbox then title will get updated with the latest value. So its all happening through two way data binding.