Prototypal Inheritance
In javascript prototypal inheritance means an object getting the access to the properties and methods of another objects.As we know arrays[] and functions() are basically object{} in javascript.So the array[] objects and function() objects get access to the properties and methods of the objects{}.
Prototypal Inheritance In Array
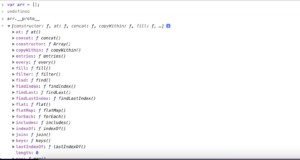
If you will see in the above diagram , when we type arr.__proto__ in console, you will be able to access all the methods of array.
Now let’s go up to the prototype chain, what is there on top of Array?
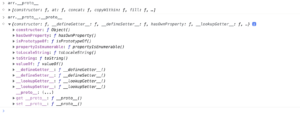 You can see its Object right?
You can see its Object right?
Have you ever think how we can access the toString() method of Array.Well we just said inheritance is an Object(array) can access methods(toString()) of another object(Object{}).
So whatever is on the top of the prototype inheritance chain, you will be able to access it.
Let’s try the same thing with functions as well.
Prototypal Inheritance In Function
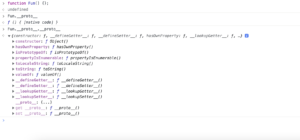
In case of function also you can see Fun.__proto__.__proto__ is nothing but the object.
Let’s try with object itself.
Prototypal Inheritance In Object
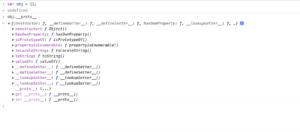 By seeing the above all diagrams can we say either it is an array or functions , ultimately they are nothing but the object.
By seeing the above all diagrams can we say either it is an array or functions , ultimately they are nothing but the object.
Example of Prototypical Inheritance
let user1 = {
name: 'John',
age: 21,
getDetails: function() {
console.log(this.name, this.age);
}
}
let user2 = {
name: 'Lee'
}
Now we want to do the same operation in user2 as well. But we don’t want to repeat the code. let’s see how user2 can get the access of user1 getDetails() method.
const getDetails = user1.getDetails.bind(user2);
So the above code is saying that we want to access the getDetails method of user1 object into the user2 object.
But wait , in getDetails method it is asking for name as well as the age. But in user2 object there is only name not the age right?
So we need to find the solution that not just lets user2 have access to getDetails method as well as the age variable.
So we basically want user2 to inherit all functions and variables(properties) of user1. it can be done using below code.
user2.__proto__ = user1;
Now lets combine all the code and see what is the output.
let user1 = {
name: 'John',
age: 21,
getDetails: function() {
console.log(this.name, this.age);
}
}
let user2 = {
name: 'Lee'
}
user2.__proto__ = user1;
console.log(user2.getDetails())
Output: "Lee", 21
Basically here we have given access to the methods and properties of user1 object to user2 object using the __proto__. Hence when we are doing the console.log for user.gerDetails() method. So its taking the name from user2 object but taking the age from user1 object as age was not present in user2. It means whatever properties user2 is already having will be taken from user2 itself. But whatever is new properties or methods will be inherited from user1.
Advantages of Prototypal Inheritance
- One of the most important advantages of prototypal inheritance is that you can add new properties to prototypes after they are created. This allows you to add new methods to a prototype which will be automatically made available to all the objects which delegate to that prototype.
- It reduces the code redundancy.
- It is very simple and powerfull.


