In Angular, a module is a way to group components, directives, pipes and services that are related, in such a way that can be combined with other modules to create an application.
What is ngModule :
Whenever we create the angular application either by using CLI or manually, the first thing we have to load the root module i.e ngModule. So by using CLI its automatically load. The purpose of a NgModule is to declare each thing you create in Angular, and group them together for example component , services, modules etc.
How root module loaded , we can see in main.ts file.
main.ts
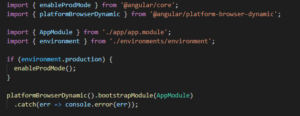
Here you can see the our bootstrap module is AppModule. And how app module looks like , lets see the below code –
app.module.ts
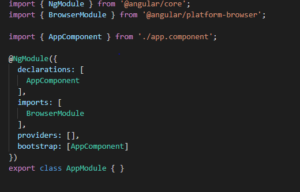
So you can see inside the @ngModule there are different metadata.
- declarations
- imports
- providers
- bootstrap
There are other metadata also which we can add inside the modules. But first lets have a look into above given things.
1. declarations : Inside the declaration section we mainly declare the components, directives and pipes. These are the things which we use in templates.
2. imports : Inside the imports section , we can import the other modules , which we can say dependent modules or features module. For example if you are using FormModule, HttpModule or any custom module in you application then you can import this module inside the imports section.
3. Providers : It is mainly used for services. Services which are declared inside this providers section , can be available globally in the application. We can specify provider at component level as well. Since Angular 6, services don’t need to be registered in a module anymore. The use of “providers” in a NgModule is now limited to overriding existing services.
4. bootstrap : It is the metadata where we can declare out bootstrapping component or root component. Means when we will run our application by default which component should load or render or bootstrap. Generally when we create the application using CLI so AppComponent is used as a bootstrap component , but we can change it as per our need.
Apart from these four metadata, there is one other metadata used in the ngModule i.e
5. exports : Inside the exports we used to declare that components which are used and visible inside the templates.
Scopes of components and services declared inside the ngModule :
- declarations / components are in local scope (private visibility),
- providers / services are (generally) in global scope (public visibility).
Components which you declared inside the ngModule are having local scope means it can be used only in current module, and if you want to use this component outside of current module then you have to export this component like below –
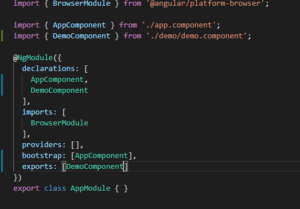
Here DemoComponent was having local scope , but we have now export it , so it can be visible on other module as well.
Services you provided will generally be available / injectable anywhere in your app, in all modules.
Conclusion : It is a very basic information about the module(ngModule) in angular. In upcoming tutorial we will see how we can create our own modules(feature module or lazyloaded module) and how we can work on that. Also we will look into other built in modules like httpModule, formModule , routerModule etc. in detail.